What is the cloud?
The cloud provides storage space, computing power, and executable software in a remote data center. The term takes into account the fact that the server is not physically accessible or directly visible to the user.
The term “cloud” is short for cloud computing. A cloud is made up of spatially-separated, remote servers, which can be reached via a secured and protected internet connection from anywhere and at any time.
Nowadays, efficient business management requires computer capacity to be flexibly adaptable so that it can be used by external employees without any problems if necessary. In addition, this flexibility also generally allows the booked service to be adapted depending on demand. In contrast, a rigid, internally-established IT structure ties up personnel and financial resources. Under certain circumstances, it may not be able to keep pace with changing requirements. A freely scalable alternative is, therefore, often the better choice.
This fact has led to the development of storage space that is remote from the actual server in workplaces; data is outsourced to the cloud, also called the “data cloud.” The storage space and programs used in the cloud can be also adapted to a company’s individual requirements in a process referred to as “scalability.”
The story of cloud computing began as early as the 1950s. Since the beginning of the internet age, the possibilities of cloud computing have continuously increased.
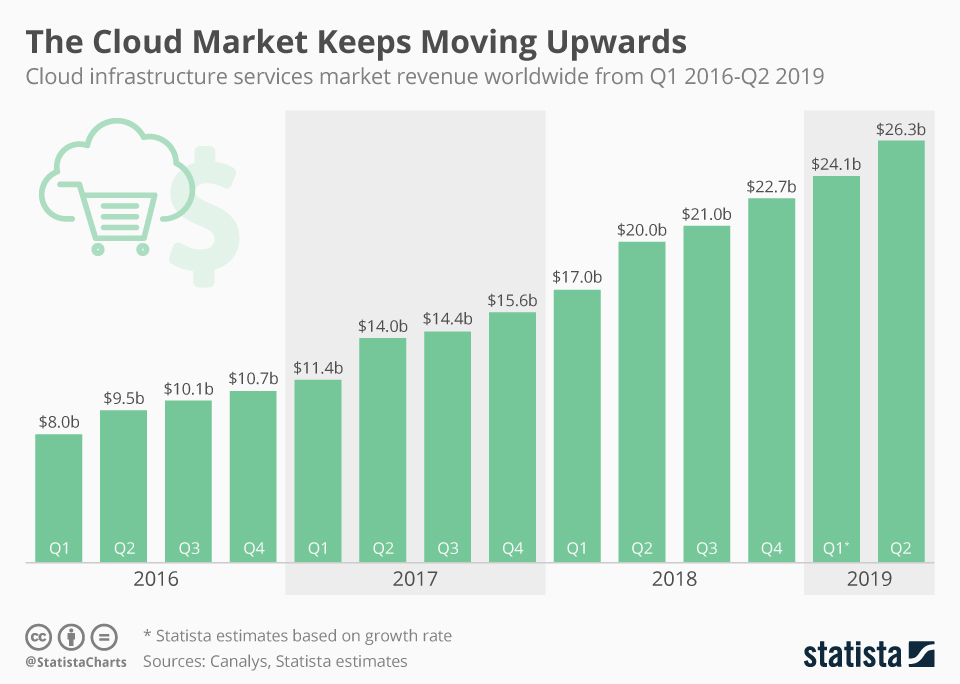 Find more infographics at Statista
Find more infographics at Statista The trend will continue as the latest internet security standards have significantly reduced previous concerns about using cloud services. It is expected that by 2025 almost two-thirds of the world's stored data will be stored and managed in a cloud solution.
You want your own Cloud Server? IONOS offers Cloud Servers with the highest performance and highest level of security. Take advantage of the IONOS free Cloud Server trial now and test your Cloud Server for free for 30 days.
What do you do with a cloud?
When you use the cloud, data, programs, and computing capacity are outsourced to storage spaces outside of the user’s location. To do this, several servers are made available in a remote location. Cloud storage offers include renting storage space and the use of computing power – in principle, the complete infrastructure of a data center. In this way, companies and private users can use programs directly via the browser, for example, without having to install them locally. Others use the cloud only for additional storage. Cloud computing is also popular among teams: many collaboration tools are based on the cloud.
Access takes place via a securely encrypted internet connection. The respective users must identify themselves in order to access the storage space. The principle is similar to a company network, but the physical distance between your workplace computer and the server is usually much greater.
Which storage size, which computing capacity, or which software is used by the cloud provider for which period of time is contractually determined. In this way, companies can flexibly choose to increase services at a later date without having to invest in additional hardware or expensive software. It also allows them to forgo regular updates while benefiting from more computing power and storage space. For private users, many services can even be used free of charge.
Via the cloud, users can store and retrieve data. Application programs (software) can also be used via the cloud: This ranges from word processing and spreadsheets to complex programs for design tasks or image processing. The contractually booked software is kept up-to-date by the cloud service provider.
Various apps are already available to synchronize data in the cloud between several stationary or mobile devices, so that the latest version of a file is always available to all authorized users. In addition, several people with access rights to a project or company can work with the data in the cloud at the same time.
An important component of cloud computing is data safety (backups). The highly-secure server farms are not only equipped with redundant storage, but are also well secured physically and thermally. In effect, all data is stored in a well-protected location and is available to users around the clock.
For automatic, encrypted backups, easy recovery, and all-around protection of all data and devices, try IONOS’ Cloud Backup software solution. Two different packages are available: Cloud Backup for up to 5 TB of data, or Cloud Backup Flex with a pay-as-you-go option based on the GB used.
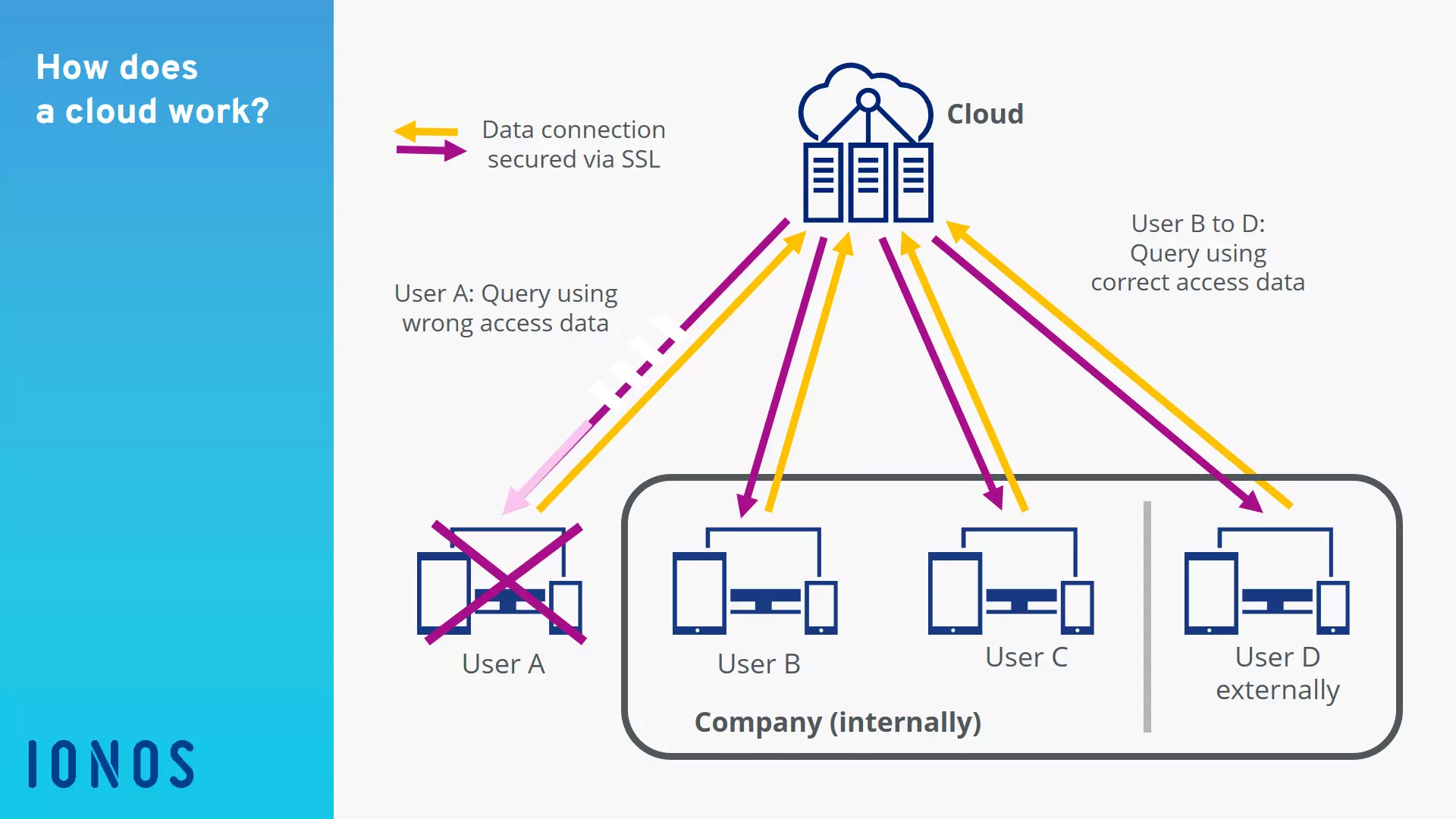
How does the cloud work?
The cloud works like the network in a company, where you have to log in from your workspace to access the company server. However, the cloud server is not located onsite, but on a server farm – far away from the company’s physical location. The hard disks, processors, and memory space “gathered” in the server are managed by special administration routines. Users access the cloud’s infrastructure and/or the contractually guaranteed software via a digital interface. In renting storage space, the user is granted access authorization. Data can be managed as on a hard disk and programs can usually be used via a web browser.
When companies provide their employees with their own servers for cloud computing, this is called a private cloud. In this way, the user has direct access to the company server on which data and services stored are not publicly available. This means that sensitive data remains accessible only to the company. In Europe, certain data may not leave the company according to the GDPR. However, a private cloud places very high demands on administration and is considered time-consuming and costly.
A public cloud makes its services available to the public via the internet. The system is monitored, maintained, and always adapted to the needs of the users by this provider. This eliminates the costs of setting up, maintaining, and continually adapting a company's internal server architecture.
A combination of both of these solutions is known as a hybrid cloud, in which sensitive data is saved in the company and other, less sensitive data is saved on a publicly-accessible platform.
How is data stored in the cloud?
In cloud computing, data is stored on the hard disk of a computer in the same way as on the hard disk of a computer through read and write access. For users, the difference is that next to the hard disk drive, for example drive DATA (D:), there is a cloud drive icon for opening and saving data. In other words, the same options are available in the cloud as on the user's own hard drive: the creation and deletion of folders and subfolders as well as the upload, saving, updating, moving, renaming, or deleting of files – and this applies to all file types. It is, therefore, also possible to safely store backups of databases or mobile devices such as smartphones or tablets there.
The data in the cloud itself is encrypted and stored redundantly (i.e. multiple times). Transmission to the cloud server and from there to the users is also carried out via a secure and encrypted connection. Internal data management between servers and security servers as well as regular backups of customer data is the responsibility of the cloud operator. With server locations within the EU, providers of cloud services are subject to the EU General Data Protection Regulation, meaning that users can assume the highest security standards.
- Automatic backup & easy recovery
- Intuitive scheduling and management
- AI-based threat protection
Under which circumstances should you use the cloud?
There is no straightforward answer like “A company needs a cloud when using X gigabytes of data.” There are many factors that speak for or against using a cloud. The cost-benefit calculation must compare financial factors including maintenance, repair, depreciation, and IT in the company with the costs of using the outsourced data and programs. This also includes a forecast of how the computing capacity in the company must develop in order to be prepared for future requirements.
When using cloud services, storage rental costs usually include a flat rate for the maintenance and backup of the servers. The hardware in the cloud is always up-to-date, including the latest data and physical security measures. Furthermore, the provision of licensed software (e.g. Microsoft Office 365) via cloud computing eliminates the need for the costly purchase of individual software licenses and updates in the company.
IONOS’ HiDrive Cloud Storage is ideal if you’re looking for a centralized data storage solution that also lets you share and edit files. This high-security, data storage is available in four different packages: Basic, Essential, Business, and Pro.
Most cloud providers offer some of the available storage space free of charge or via hosting contracts. This allows companies to test a cloud solution before deciding on large-scale, paid solutions.
However, the use of cloud computing adds a great deal of responsibility for authorized users, as they must strictly adhere to the company's security standards to protect company secrets from unauthorized access. It is, therefore, advisable to define rights clearly and to keep proper documentation.
- Store, share, and edit data easily
- Backed up and highly secure
- Sync with all devices