What is Storage Spaces Direct (S2D)?
Every hard disk runs out of space at some point. Put simply, Storage Spaces Direct is a method of grouping together multiple hard disks into a logical volume that resembles a single disk to the user. With S2D, users no longer have to worry about the physical location of their data, since the S2D file system is automatically managed by the servers. This means that the components used in the system must be highly resilient.
Storage Spaces Direct allows you to combine the data storage devices of different Windows servers into a single storage cluster and subdivide them into virtual disks that are shared with users. The software takes control of the drives, which has certain implications for the hardware you choose for S2D.
Cost-effective, scalable storage that integrates into your application scenarios. Protect your data with highly secure servers and individual access control.
Prerequisites for Storage Spaces Direct (S2D)
Storage Spaces Direct (S2D) is a software-defined storage solution in Windows Server 2016, meaning that it doesn’t run on every Windows PC. The technology is based on Storage Spaces, which Microsoft introduced in Windows Server 2012. At the time, Storage Spaces still included Scale-Out File Server (SOFS), a file server with horizontal scalability.
To use Storage Spaces Direct (S2D), you need multiple hard drives on a single server or multiple servers, each with one or more hard drives. The servers can be connected over Ethernet, meaning no special cables are required. Traditional hard drives (HDD), SSD or NVMe memory cards can be used as drives.
Storage Spaces Direct is abbreviated S2D. This is mainly because the abbreviation SSD is already taken. SSD stands for Solid State Drive, a well-known type of semiconductor memory. To the user, SSDs look like any other disk, but unlike conventional hard drives, they do not have mechanical components.
Choosing the right hardware components for Storage Spaces Direct (S2D)
All devices must be Windows Server 2016 Certified by Microsoft for use with Storage Spaces Direct. This ensures the hardware you use will interact seamlessly. Microsoft provides a list of preconfigured servers suitable for Windows Server 2016 – so called hyperconverged systems.
You can also choose your own combination of suitable components for your specific use case. If you choose to do so, use components certified by Microsoft for compliance with the Software-Defined Data Center (SDDC) standard.
Intel Nehalem or comparable AMD EPYC processors meet the minimum requirements for server compatibility. A Storage Spaces Direct node requires 4 GB of RAM per TB per cache drive, in addition to the Memory for a single Windows Server with the same requirements.
Hard drives and SSDs can be attached via SAS or SATA. USB drives are not supported. Similarly, RAID controllers cannot be used since the hardware is controlled exclusively via the Storage Spaces Direct software layer. The drives must be physically connected to the server. Network Attached Storage (NAS) cannot be integrated.
If you want to store data that is accessed or changed frequently, you should install SSDs in the servers. In this case, you have to use Enterprise SSDs that support power loss protection, meaning they will not generate errors in the file system if the power supply fails. When using SSDs or NVMe drives, all drives installed in a node must be of the same type.
Network infrastructure for Storage Spaces Direct (S2D)
The individual nodes within a cluster require a 10 Gbps or faster network connection to communicate with each other. Network cards must support RDMA (Remote Direct Memory Access) with the RoCE or iWARP protocols. The usual requirements for Windows server-based networks apply when it comes to connecting workstations to the network.
What does Storage Spaces Direct (S2D) consist of?
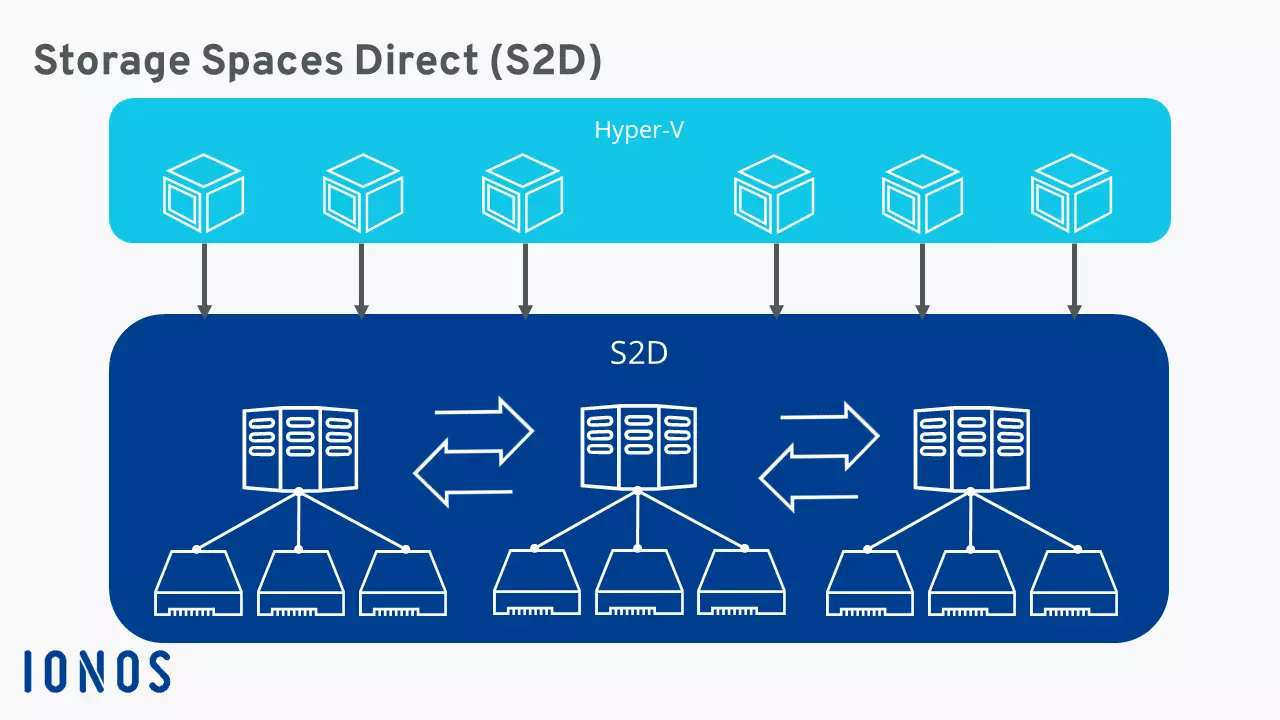
Storage Spaces Direct consists of at least two nodes. It uses Microsoft-approved standard server hardware that runs Windows Server 2016. At least two drives are installed on each of these nodes. To protect against hardware failures, the Failover Clustering feature must be installed in Windows Server 2016.
When is Storage Spaces Direct (S2D) used?
Storage Spaces Direct is ideal when you want to expand network storage capacity in the most flexible way possible and ensure that data is highly secure in the event of hardware failures. S2D allows you to make data available at different company locations at the same time, assuming you have a fast network connection between these locations.
You can also use Storage Spaces Direct to make hyper-V machines in your network more scalable. With S2D, multiple virtual machines can access the same data.
How does Storage Spaces Direct (S2D) work?
Storage Spaces Direct (S2D) is a software-defined storage solution in which a software application manages the storage hardware. This allows you to pool storage capacity and combine the technical advantages of the individual drives, even if they are in different locations and connected to different servers. S2D groups together servers and storage media into a single Storage Space Direct cluster.
If you use different storage technologies, the software automatically decides which data is stored on which hardware. Files used frequently are stored on fast NVMe storage media, files that are regularly edited are stored on SSDs, and backup files or rarely used files are stored on conventional hard drives. Ideally, SSD or NVMe storage devices should also be used as cache drives. To users in the network, the whole cluster looks like a network share. That means you don’t have to worry about which data is on which hardware.
The IONOS Enterprise Cloud makes software-defined storage technology accessible to small and medium-sized companies that do not operate their own servers. This business cloud gives you the flexibility to scale your required resources at any time using the patented Data Center Designer.
You can manage servers using the “Server Manager” console in the Windows Server 2016 operating system or from Command Prompt. When you install the Storage Spaces Direct cluster, all hard disks of the different servers are aggregated into a single storage pool. It’s important to ensure that the cluster includes only those drives that store user data. The operating system drives of the servers remain independent.
Usable hard disks and solid-state drives are automatically detected and added. In this way, you can add more hard drives and servers to the cluster later and scale storage capacity as needed. In addition to the system hard disk, up to four data drives and two cache drives can be installed in each node.
Virtual disks called cluster shared volumes (CSV) can then be created in the new cluster. These CSVs are then formatted using one of two files systems. Microsoft recommends CSV-ReFS (Resilient File System), which is more suitable for Storage Spaces Direct technology than CSV-NTFS, that is based on the default NTFS file system for hard disks. The CSVs can span multiple physical disks, which is of no concern to the user because everything is managed by the system.
Each individual Storage Spaces Direct node can have a total storage capacity of up to 100 TB. A storage pool consisting of multiple servers can only have a maximum capacity of 1 PB (one petabyte = 1,024 TB), although Storage Spaces Direct (S2D) allows up to 16 servers.
The individual network nodes communicate using the SMB3 protocol, an enhanced version of the Server Message Block (SMB) protocol that includes SMB Direct and SMB Multichannel.
It’s also possible to combine multiple hard disks into one disk on a Windows PC. You can use dynamic disks for this purpose. In Windows 10 Disk Management, existing hard drives can be converted into dynamic disks. They can then be combined into one logical drive. Automatic mirroring of data is also possible. However, this cannot be undone without reformatting the drive.
How do you ensure fault tolerance with Storage Spaces Direct (S2D)?
Thanks to the Failover Clustering feature in Windows Server 2016, Storage Spaces Direct has built-in methods of protecting stored data from hardware failures. If a hard disk or an entire node fails, no data is lost and the system as a whole remains operational. In most cases, users are unaware of the hardware failure.
If only two nodes are combined into a cluster, two-way mirroring is used. This synchronizes the data of both nodes so one node or one disk could fail completely. Three-way mirroring is recommended for three nodes or more. Then, one of three nodes can fail completely and multiple drives can stop working on another node. If 50% of drives are affected at the same time, data consistency cannot be ensured. Failure of an operating system hard drive is equivalent to a server failure.
Advantages of Storage Spaces Direct (S2D) at a glance
- Good scalability, more servers can be easily added.
- High availability through mirroring of data; hardware failures do not result in data loss.
- Unlike similar solutions from other vendors, S2D allows you to use industry-standard server hardware as long as it is approved by Microsoft.
- The system is optimized for SQL servers and virtualization with Hyper-V.