Kubernetes Tutorial for Beginners
The Kubernetes software enables you to manage large quantities of containers and helps you with a range of automatic functions. In this way, Kubernetes – also known as K8s – has created a mini revolution in software development. To benefit from this system, we take you through the most important steps – from installation through to your first cluster.
The ideal platform for demanding, highly scalable container applications. Managed Kubernetes works with many cloud-native solutions and includes 24/7 expert support.
Kubernetes: Installation & Getting Started
Kubernetes works with various servers: masters and nodes. They don’t necessarily have to be on separate physical servers. Virtual machines also enable you to activate multiple Kubernetes nodes on a computer. The free program Minikube has proved to be especially effective for test purposes. It also allows you to work with Kubernetes locally. Since Minikube creates a virtual machine, the program requires a hypervisor. To use it, you’ll therefore need to have installed a program like VirtualBox. The Kube Control tool is also necessary.
This Kubernetes tutorial explains the installation steps for Ubuntu. But it’s also possible to run Kubernetes on Windows or macOS. The official guide also contains solutions in this regard.
Installing Kube Control
First, install Kubectl on your system. You’ll need this program to manage clusters.
curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/$(curl -s https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectlMinikube
Next, install Minikube – a tool that creates a virtual machine as a node.
curl -Lo minikube https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/minikube-linux-amd64 \
&& chmod +x minikubeNow launch Minikube.
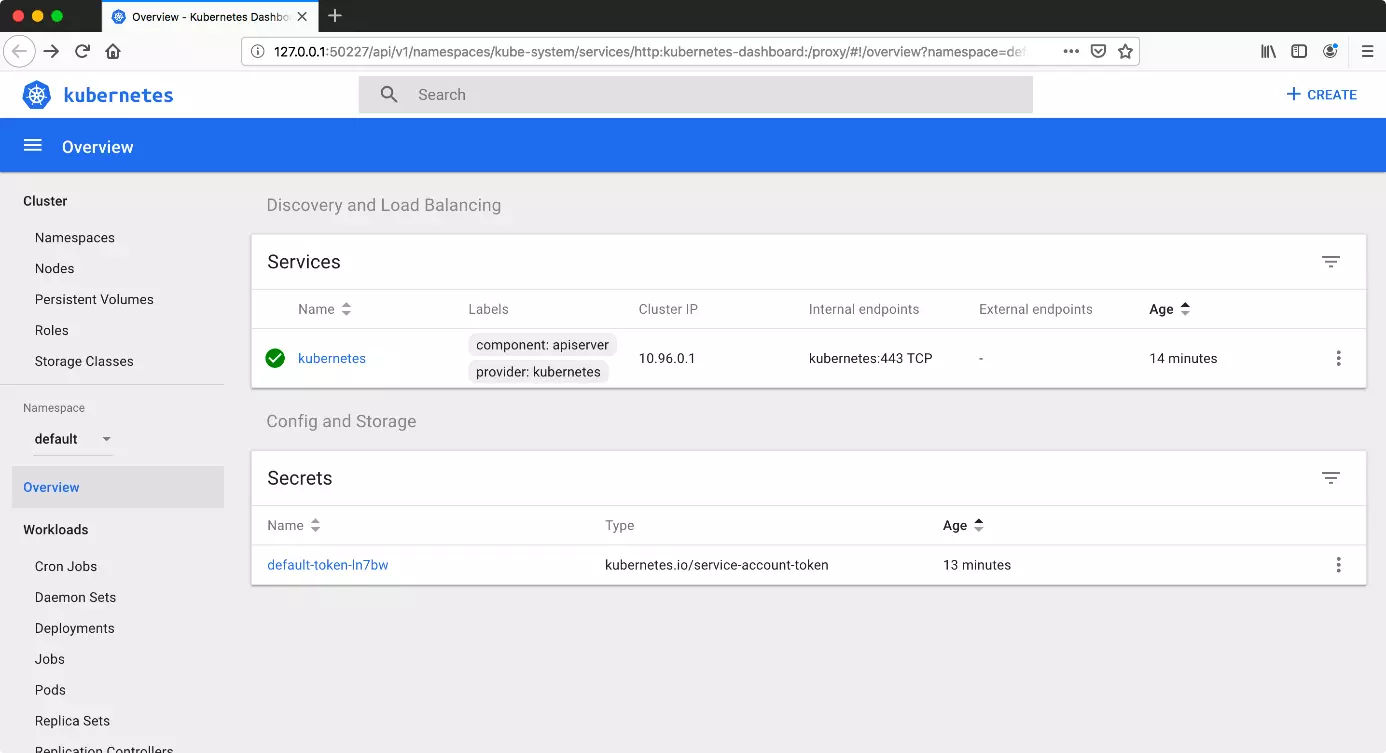
minikube startWhen you start Minikube, Kubectl should automatically be configured correctly. Enter another command to switch from the command line to a GUI. This opens the dashboard in the standard browser.
minikube dashboardIf you wish to go without installing Kubernetes on your system, you can also access a developers’ web terminal. Here, you can then learn the ins and outs of Kubernetes using an interactive tutorial.
Using Kubernetes
After starting Minikube, the program automatically creates a cluster with a single node. You can check it with a Kubectl query:
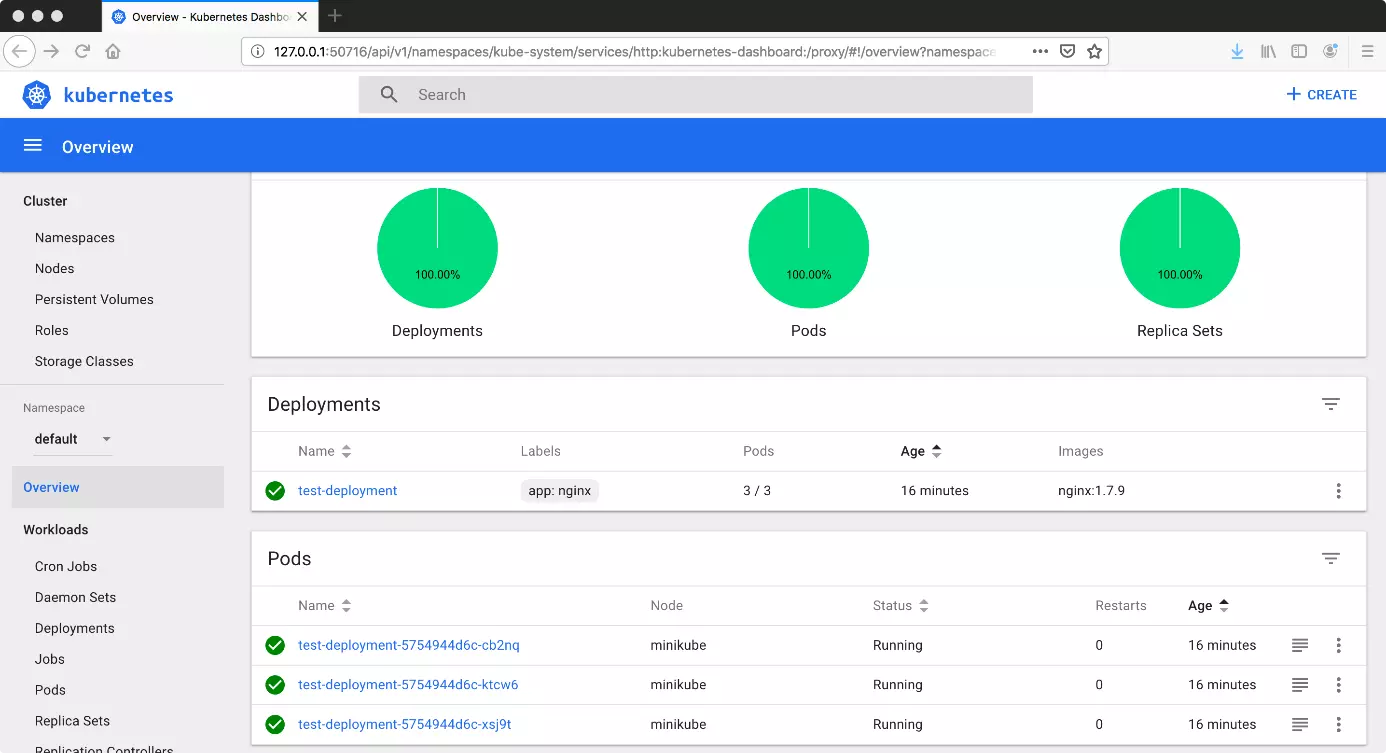
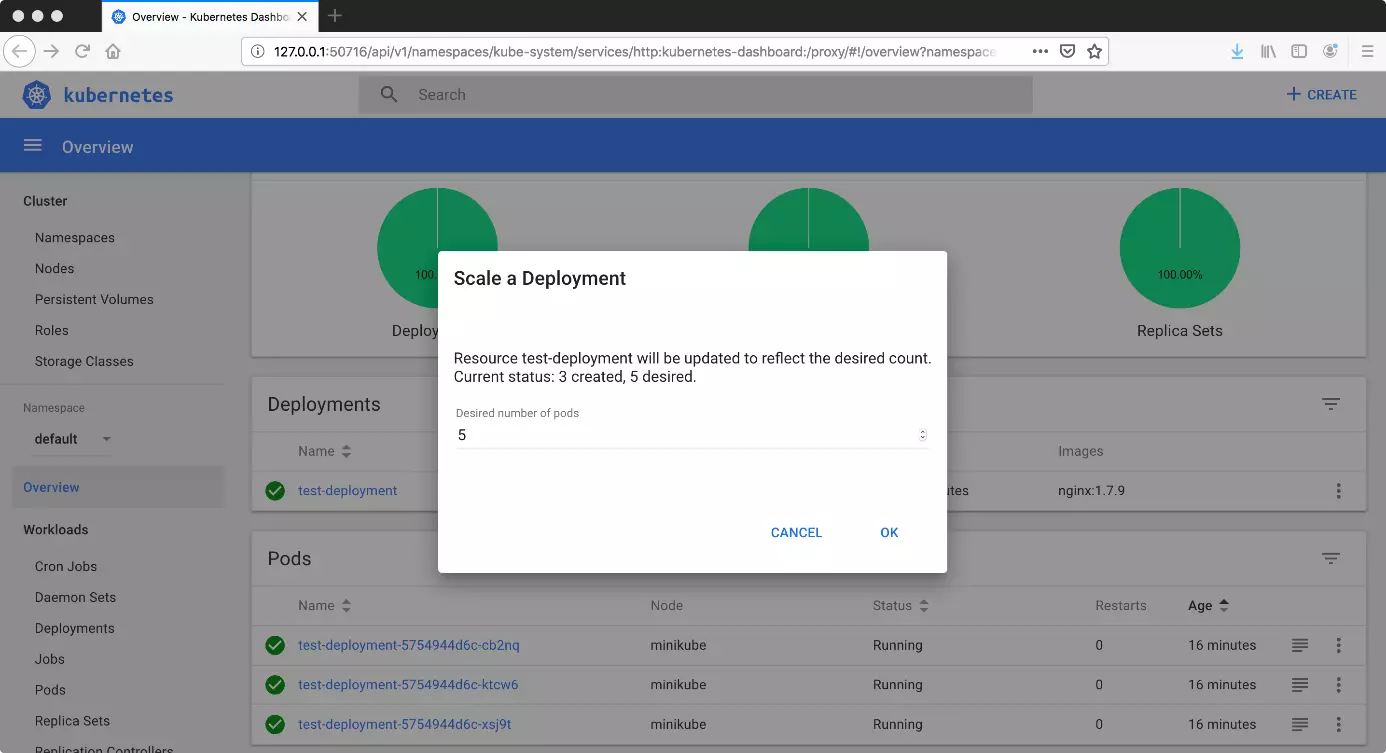
kubectl get nodesYou can create deployments using the dashboard. Click on the “Create” button (top right) to access an online editor. There you’ll be able to create a deployment in JSON or YAML format. Once you’ve done this, Kubernetes will automatically generate multiple pods. You can adjust the desired amount by scaling the deployment. This function is located next to the deployment in the form of a “more options” button (with three dots).
kubectl create deployment --image=[pathway to image]You can pull up a range of information using the command line.
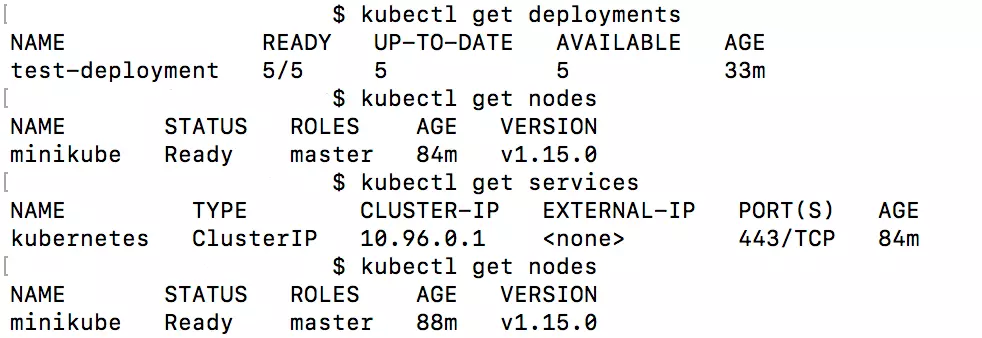
What deployments are there?
kubectl get deploymentsHow many pods are there?
kubectl get podsWhat services are there?
kubectl get servicesWhich nodes are active?
kubectl get nodeskubectl expose deploy test-deploymentHowever, entering this code only releases the service within the cluster. In order to access the deployment beyond the cluster, extra flags are necessary:
kubectl expose deploy test-deployment --type=LoadBalancer --port=8080You can then start the service with Minikube:
minikube service test-deploymentIf you want to delete the service again, there’s also a command for that:
kubectl delete service test-deploymentThe deployment can also be deleted:
kubectl delete deployment test-deploymentIn order to end Minikube, you need to stop the process:
minikube stopAnd if you no longer wish to work with the virtual machine, you can also remove that.
minikube deleteAfterwards, any configured settings as well as created deployments and pods will also be deleted. If you launch Minikube again, you’ll start with an empty cluster again.
- Cost-effective vCPUs and powerful dedicated cores
- Flexibility with no minimum contract
- 24/7 expert support included